Bashkortostan
| Republic of Bashkortostan (English) Республика Башкортостан (Russian) Башҡортостан Республикаһы (Bashkir) |
|
|---|---|
| - Republic - | |
.svg.png) |
|
 Coat of arms of Bashkortostan |
 Flag of Bashkortostan |
| Anthem | National Anthem of the Republic of Bashkortostan |
| Political status | |
| Country | Russia |
| Political status | Republic |
| Federal district | Volga[1] |
| Economic region | Urals[2] |
| Capital | Ufa |
| Official languages | Russian[3]; Bashkir[4] |
| Statistics | |
| Population (2002 Census)[5] | 4,104,336 inhabitants |
| - Rank within Russia | 7th |
| - Urban[5] | 64.0% |
| - Rural[5] | 36.0% |
| - Density | 28.58 /km2 (74.0 /sq mi)[6] |
| Area (as of the 2002 Census)[7] | 143,600 km2 (55,444.3 sq mi) |
| - Rank within Russia | 27th |
| Established | March 23, 1919 |
| License plates | 02 |
| ISO 3166-2:RU | RU-BA |
| Time zone | YEKT/YEKST (UTC+5/+6) |
| Government (as of October 2008) | |
| President[8] | Rustem Khamitov |
| Legislature | State Assembly—Kurultai[8] |
| Constitution | Constitution of the Republic of Bashkortostan |
| Official website | |
| http://www.bashkortostan.ru | |
The Republic of Bashkortostan (Russian: Респу́блика Башкортоста́н; Bashkir: Башҡортостан Республикаһы) or Bashkiria (Башки́рия) is a federal subject of Russia (a republic). It is located between the Volga River and the Ural Mountains. Its capital is Ufa.
Contents |
Terminology
The direct romanization of the republic's name in Russian is Respublika Bashkortostan or Bashkiriya, and the romanization of the republic's name in Bashkir is Başqortostan Respublikahı.
History
The first settlements in the territory of modern Bashkortostan were set up in the early Paleolithic period; however, it was the Bronze Age which served as a spur to populate this territory. When people of Abashevo culture started settling here, they possessed high skills in manufacturing bronze tools, weapons, and decorations. They were the first to establish permanent settlements in the Southern Urals. The ethnonym Bashkirs first became known in the 9th century.
In the 10th century, Islam started to spread among Bashkirs, and in the 14th century it became a dominant religion. Up to the 16th century the territory of modern Bashkortostan was divided between Kazan and Siberia Khanates and Nogai Horde. The tribes that lived there were headed by bi (tribal heads). After Kazan fell to Ivan the Terrible in 1554–1555, representatives of western and north-western Bashkir tribes approached the Tsar with a request to voluntarily join the Muscovy.
Starting from the second half of the 16th century, Bashkiria's territory began taking shape as a part of the Russian state. In 1798 the Spiritual Assembly of Russia Muslims was established—an indication that the tsarist Government recognized the rights of Bashkirs, Tatars, and other Muslim nations to profess Islam and perform religious rituals. Ufa Governorate (guberniya), with a center in Ufa, was formed in 1865—another step towards territorial identification.
After the Russian revolution, Bashkir Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (ASSR) within the Russian SFSR was established in 1919, firstly as Little Bashkortostan, but then all Ufa Governorate was incorporated to the newly established republic. During the Soviet period, Bashkiria was granted broad autonomous rights—the first among other Russian regions. The administrative structure of the Bashkir ASSR was based on principals similar to those of other autonomous republics of Russia.
The extraction of Bashkir crude oil began in 1932. At the end of 1943, large crude oil deposits (Tuymazy oil-field) were discovered. During the World War II, Bashkiria became one of the major regions of the Soviet Union to accommodate plants and factories evacuated from Western Russia, as well as great masses of people, as well as providing the country with weaponry, fuel, and food-stuffs. After the war, a good number of industries were further developed in Bashkiria such as mining, machine building and, especially, oil-refining. Bashkiria's industry became a solid basis for further economic growth of all European outlying territories of Russia.
On October 11, 1990 the Supreme Soviet of the Republic adopted the Declaration on state sovereignty of the Bashkir ASSR. On February 25, 1992 the Bashkir ASSR was renamed the Republic of Bashkortostan.
On March 31, 1992 a Federative Compact "On separation of authorities and powers among federal organs of power of the Russian Federation and the organs of power of the Republic of Bashkortostan" was signed. On August 3, 1994 a Compact "On separation of authorities and mutual delegating of powers among the organs of power of the Russian Federation and the organs of power of the Republic of Bashkortostan" was signed.
Politics
The head of the government of Bashkortostan is the President, who is appointed by the President of Russia for a four-year term. According to the Constitution, the President of the Republic of Bashkortostan guarantees rights and liberties of a person and a citizen, protects economic and political interests of the Republic of Bashkortostan, and secures legitimacy, law and order on its territory.
As of 2007, the president is Murtaza Rakhimov, who was elected on December 17, 1993. Before the elections, Rakhimov was the Chairman of the Supreme Soviet of the Republic—the highest post at that time. Rakhimov was re-elected in December 2003 in a poll condemned by the OSCE for exhibiting "elements of basic fraud."
The Republic's parliament is the State Assembly—Kurultai, popularly elected every five years. The one-chamber State Assembly has 120 deputies.
The Republic's Constitution was adopted on December 24, 1993. Article 1 of the Constitution stipulates that Bashkortostan is a sovereign state within Russia, it has all the state power in full volume beyond the limits of authority of the Russian Federation and the powers of the Russian Federation concerning the aspect of joint authority of the Russian Federation and the Republic of Bashkortostan. The Republic of Bashkortostan is a full-fledged subject of the Russian Federation on equal and agreed bases.
The relations of the Republic of Bashkortostan and the Russian Federation are at present based on the articles of the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Constitution of the Republic of Bashkortostan, the Federative Compact (with amendments), the Agreement on Separation of authorities and powers and mutual delegating of powers among the organs of state power of the Republic of Bashkortostan.
The judicial power of the Republic is in the hands of courts: the Constitutional Court, the Supreme Court, the Court of Appeals, district Courts, and justices of the peace.
In full accord with universally recognized principles of international law, articles of European Charter on local self-government and the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Republic of Bashkortostan ensures in its Constitution that local self-government is recognized and guarantied on the republic territory.
The Republic of Bashkortostan resolves all the issues of its administrative-territorial structure on its own. The list of districts and towns of the republican importance, municipalities as well as the order of establishing, amending and changing borders of municipalities and their names are stipulated by the Republic of Bashkortostan law "On administrative-territorial structure of the Republic of Bashkortostan and territory of municipalities".
Economy
Much of Bashkortostan's economy depends on its oil processing industry, which is a left-over from Soviet times and has seen little investment since the collapse of the Soviet Union. Most of the industry, nominally privatized, has in fact been granted to the factions close to the president's family.
More than half of Bashkortostan's industry is based in Ufa, the republic's capital.
| 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gross regional product | 214.8 | 279.7 | n/a | billion roubles | |
| Industrial production volume | 161.7 | 192.1 | 354 | billion roubles | |
| Construction | 1,408 | 1,471.5 | 1508.4 | th.m.² | |
| Agricultural produce | 50.1 | 52.1 | 57.2 | billion roubles | |
| Investments into fixed capital | 52.1 | 53.7 | 62.4 | billion roubles | |
| Accumulated foreign investments | 71.7 | 97.6 | 157.1 | million US$ | |
| Foreign trade turnover | 2646 | 3045.3 | 3840.6 | million US$ | |
| Export | 2303.4 | 2724.4 | 3525.9 | million US$ | |
| Import | 342.3 | 320.9 | 314.7 | million US$ | |
| Wholesale trade turnover | 117.7 | 118.1 | 151.2 | billion roubles |
Geography
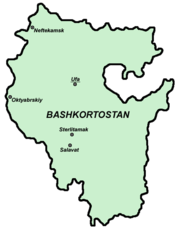
Bashkortostan contains part of the southern Urals and the adjacent plains.
- Area: 143,600 km² (according to the 2002 Census) or 142,900 km² (according to Bashkortostanstat[9])
- Borders: Bashkortostan borders Perm Krai (N), Sverdlovsk Oblast (NE), Chelyabinsk Oblast (NE/E/SE), Orenburg Oblast (SE/S/SW), Tatarstan (W), and Udmurtia (NW).
- Highest point: Mount Yamantaw (1,638 m).
- Maximum N->S distance: 550 km.
- Maximum E->W distance: over 430 km.
- Average elevation: no data.
Bashkortostan is traversed by the northeasterly line of equal latitude and longitude.
Rivers
There are over 13,000 rivers in the republic. Many rivers are parts of deepwater transportation system of European Russia; they provide access to ports of the Baltic and the Black seas.
Major rivers include:
- Belaya (Aghidhel) River (1,430 km)
- Ufa (Qaraidel) River (918 km)
- Sakmara River (760 km)
- Ik (Iq) River (571 km)
- Dyoma River (556 km)
- Ay River (549 km)
- Yuruzan River (404 km)
- Bystry Tanyp River (345 km)
- Sim River (239 km)
- Nugush River (235 km)
- Tanalyk River (225 km)
- Zilim River (215 km)
- Syun River (209 km)
Lakes
There are 2,700 lakes and reservoirs in the republic. Major lakes and reservoirs include:
- Asylykül Lake (23.5 km²)
- Qandrykül Lake (15.6 km²)
- Urgun Lake (12.0 km²)
- Pavlovskoye Reservoir (120.0 km²)
- Nugushkoye Reservoir (25.2 km²)
Mountains
The republic contains part of the southern Urals, which stretch from the northern to the southern border. The highest mountains include:
- Mount Yamantaw (1,638 m)
- Mount Bolshoy Iremel (1,582 m)
- Mount Maly Iremel (1,449 m)
- Mount Arwyakryaz (1,068 m)
- Mount Zilmerdaq (909 m)
- Mount Alataw (845 m)
- Mount Yurmataw (842 m)
Natural resources
The Republic of Bashkortostan is one of the richest territories of Russia in mineral resources. with deposits of some 3,000 mineral resources. Bashkortostan is rich in crude oil reserves, and was one of the principal centers of oil extraction in the Soviet Union. Other major resources are natural gas, coal, ferrous metal ores, manganese, chromite, iron ores, non-ferrous metals ores (lead, tungsten), non-metallic ores (rock crystal, fluorite, iceland spar, sulfide pyrites, barite, silicates, silica, asbestos, talcum), deposits of precious and semi-precious stones and natural stones (malachite, jade, granite).
The republic has enough mineral resources to provide its power and fuel complex as well as petro-chemical, chemical, agro-industrial complex, ferrous and non-ferrous metallurgy, glass-making and ceramic branches with raw materials.
Bashkortostan is one of the major raw materials bases for Russia non-ferrous metallurgy. The republic has good deposits of lignite with a high degree of bitumenosity. This lignite can be used for obtaining a variety of different chemical products like resins, surface-active substances, gummy fertilizers, and other stimulants for plants growth. Mining-chemical raw materials (rock salt, lime, phosphorites, barytes, etc.) are quite substantial, and are utilized in the republic economy.
Bashkortostan is also rich in woods. The total territory covered with forests is about 62,000 square kilometers (24,000 sq mi). More than one third of the republic territory is covered with woods. The following types of trees dominate: birch tree, conifers, lime, oak, and maple. The general stock of timber according to some evaluation is 717.9 million m³. Bashkortostan forests have special sanctuaries and national parks. They cover more than 10,000 square kilometers (4,000 sq mi).
Bashkortostan is also rich in springs and sources of mineral, medicinal, and drinking water.
Climate
- Average annual temperature: 0.3 °C (mountains) to 2.8 °C (plains)
- Average January temperature: −16 °C (3.2 °F)
- Average July temperature: +18 °C (64.4 °F)
Administrative divisions
Demographics
- Population: 4,104,336 (2002)
- Urban: 2,626,613 (70.8%)
- Rural: 1,477,723 (29.2%)
- Male: 1,923,233 (46.9%)
- Female: 2,181,103 (53.1%)
- Females per 1000 males: 1,134
- Average age: 35.6 years
- Urban: 35.2 years
- Rural: 36.4 years
- Male: 33.4 years
- Female: 37.7 years
- Number of households: 1,429,004 (with 4,066,649 people)
- Urban: 931,417 (with 2,592,909 people)
- Rural: 497,587 (with 1,473,740 people)
- Vital statistics
| Births | Deaths | Birth rate | Death rate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1970 | 63,498 | 28,004 | 16.6 | 7.3 |
| 1975 | 63,096 | 31,802 | 16.5 | 8.3 |
| 1980 | 67,743 | 36,067 | 17.6 | 9.4 |
| 1985 | 76,839 | 39,101 | 19.9 | 10.1 |
| 1990 | 63,899 | 38,157 | 16.2 | 9.7 |
| 1991 | 58,240 | 39,638 | 14.7 | 10.0 |
| 1992 | 53,271 | 43,539 | 13.3 | 10.9 |
| 1993 | 46,772 | 50,738 | 11.6 | 12.6 |
| 1994 | 47,296 | 54,267 | 11.7 | 13.4 |
| 1995 | 45,622 | 51,734 | 11.2 | 12.7 |
| 1996 | 45,228 | 49,600 | 11.1 | 12.1 |
| 1997 | 43,776 | 49,354 | 10.7 | 12.0 |
| 1998 | 44,465 | 48,470 | 10.8 | 11.8 |
| 1999 | 41,368 | 52,608 | 10.0 | 12.8 |
| 2000 | 41,642 | 53,550 | 10.1 | 13.0 |
| 2001 | 42,793 | 55,001 | 10.4 | 13.4 |
| 2002 | 45,481 | 57,836 | 11.1 | 14.1 |
| 2003 | 45,583 | 58,237 | 11.1 | 14.2 |
| 2004 | 45,733 | 57,726 | 11.2 | 14.1 |
| 2005 | 44,094 | 57,787 | 10.8 | 14.2 |
| 2006 | 45,055 | 55,319 | 11.1 | 13.6 |
| 2007 | 51,453 | 55,144 | 12.7 | 13.6 |
| 2008 | 54,493 | 55,568 | 13.4 | 13.7 |
- Ethnic groups

According to the 2002 Census the ‘national composition’ was • Russian 36.32% • Bashkir 29.76% • Tatar 24.14% • Chuvash 2.86% • Mari 2.58% • Ukrainian 1.35% • Mordovian 0.63% • Udmurt 0.55% • Belarusians 0.42% • Armenian 0.21% • German 0.20% • Uzbek 0.13% • Azeri 0.12% • Kryashen 0.11% • Kazakh 0.10% • Tajik 0.07% • Jewish 0.06% • and various other groups of less than two thousand persons each. An additional 0.11% of the inhabitants declined to state their nationality on the census questionnaire.[10] Historical figures are shown below:
| census 1926 | census 1939 | census 1959 | census 1970 | census 1979 | census 1989 | census 2002 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bashkirs | 625,845 (23.5%) | 671,188 (21.2%) | 737,744 (22.1%) | 892,248 (23.4%) | 935,880 (24.3%) | 863,808 (21.9%) | 1,221,302 (29.8%) |
| Russians | 1,064,707 (39.9%) | 1,281,347 (40.6%) | 1,418,147 (42.4%) | 1,546,304 (40.5%) | 1,547,893 (40.3%) | 1,548,291 (39.3%) | 1,490,715 (36.3%) |
| Tatars | 621,158 (23.3%) | 777,230 (24.6%) | 768,566 (23.0%) | 944,505 (24.7%) | 940,436 (24.5%) | 1,120,702 (28.4%) | 990,702 (24.1%) |
| Chuvash | 84,886 (3.2%) | 106,892 (3.4%) | 109,970 (3.3%) | 126,638 (3.3%) | 122,344 (3.2%) | 118,509 (3.0%) | 117,317 (2.9%) |
| Mari | 79,298 (3.0%) | 90,163 (2.9%) | 93,902 (2.8%) | 109,638 (2.9%) | 106,793 (2.8%) | 105,768 (2.7%) | 105,829 (2.6%) |
| Ukrainians | 76,710 (2.9%) | 99,289 (3.1%) | 83,594 (2.5%) | 76,005 (2.0%) | 75,571 (2.0%) | 74,990 (1.9%) | 55,249 (1.3%) |
| Others | 113,232 (4.2%) | 132,860 (4.2%) | 129,686 (3.9%) | 122,737 (3.2%) | 115,363 (3.0%) | 111,045 (2.8%) | 123,222 (3.0%) |
Spoken languages: Russian (~100%), Tatar (34%), Bashkir (26%).[11]
Religion
Adherents of Islam account for the majority of Bashkir and Tatar. Most Russians, Chuvash, Mari and Ukranians are Orthodox Christians. Non-religious people form a substantial part of any ethnic group in Bashkortostan.
There are 13,000 Jews in the republic, with a historic synagogue in Ufa, and a new Jewish Community Center built in 2008.[12]
Population development
| Year | Population |
|---|---|
| 1897 | 1,991,000 |
| 1913 | 2,811,000 |
| 1926 | 2,547,000 |
| 1939 | 3,158,000 |
| 1959 | 3,340,000 |
| 1970 | 3,818,000 |
| 1979 | 3,849,000 |
| 1989 | 3,950,000 |
| 2002 | 4,104,000 |
| 2005 | 4,078,800 |
Education
The Republic of Bashkortostan possesses high scientific and technical potential. About 60 scientific organizations are active in Bashkortostan. Fundamental and applied scientific research work is under way at 12 Institutes UFA Scientific Center of the Russian Academy of Sciences, 29 Institutes of different branches of industry as well as design bureaus and organizations, chairs of universities and colleges.
The system of popular upbringing and teaching among Bashkir people took shape for centuries and its reflected in folklore, national customs, and traditions. When Islam spread in Bashkiria in the 10th century, the school education began to emerge gradually — religious schools were set under the supervision of mosques (maktabeh and madrasah).
Currently the Republic of Bashkortostan is the subject of the Russian Federation with versatile network of educational establishment. 12 higher educational establishments operate in the republic as well as 16 branches of leading Russian universities and colleges. Specialists graduate from them in about 200 trades and professions.
Education is primarily in Russian, Bashkir, and Tatar.
Culture
Folklore singing and dancing companies, a network of national theaters, museums, and libraries are on the rise; annual folk festivals became a tradition here.
Bashkortostan holds a leading position among all other Russian federal subjects on a number of museums, public libraries, book stocks, and municipal clubs.
The republic has seven Bashkir, four Russian, and two Tatar State Drama Theaters, the State Opera and Ballet Theater, the National Symphony Orchestra, "Bashkortostan" film-studio, thirty philharmonic collectives. The Bashkir state Folk dance ensemble named after F. Gaskarov is well-known.
The fame of Bashkir school of dancing is world renowned—many of the students get high international awards at competitions in Russia and other countries. World-renowned ballet dancer Rudolf Nureyev, as a child, was encouraged to dance in Bashkir folk performances and began his dancing career in Ufa.
Three state programs in the cultural sphere have been adopted:
- the program for further development of art and culture up to 2005;
- "Peoples of Bashkortostan" Program for the years 2003–2012;
- the Program for further study, revival and growth of folklore of Bashkortostan peoples.
See also
- Bashkirs
- Music of Bashkortostan
- Bashkir Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
- Idel-Ural State
- Zeki Velidi Togan
References
- ↑ Президент Российской Федерации. Указ №849 от 13 мая 2000 г. «О полномочном представителе Президента Российской Федерации в федеральном округе». Вступил в силу 13 мая 2000 г. Опубликован: "Собрание законодательства РФ", №20, ст. 2112, 15 мая 2000 г. (President of the Russian Federation. Decree #849 of May 13, 2000 On the Plenipotentiary Representative of the President of the Russian Federation in a Federal District. Effective as of May 13, 2000).
- ↑ Госстандарт Российской Федерации. №ОК 024-95 27 декабря 1995 г. «Общероссийский классификатор экономических регионов. 2. Экономические районы», в ред. Изменения №5/2001 ОКЭР. (Gosstandart of the Russian Federation. #OK 024-95 December 27, 1995 Russian Classification of Economic Regions. 2. Economic Regions, as amended by the Amendment #5/2001 OKER. ).
- ↑ According to Article 68.1 of the Constitution of Russia, Russian is the official language on the whole territory of the Russian Federation. Article 68.2 further stipulates that only the republics have the right to establish official languages other than Russian.
- ↑ Constitution, Article 1
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек (Population of Russia, its federal districts, federal subjects, districts, urban localities, rural localities—administrative centers, and rural localities with population of over 3,000)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://perepis2002.ru/ct/html/TOM_01_04_1.htm. Retrieved 2010-03-01.
- ↑ The value of density was calculated automatically by dividing the 2002 Census population by the area specified in the infobox. Please note that this value may not be accurate as the area specified in the infobox is not necessarily reported for the same year as the Census (2002).
- ↑ Федеральная служба государственной статистики (Federal State Statistics Service) (2004-05-21). "Территория, число районов, населённых пунктов и сельских администраций по субъектам Российской Федерации (Territory, Number of Districts, Inhabited Localities, and Rural Administration by Federal Subjects of the Russian Federation)" (in Russian). Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года (All-Russia Population Census of 2002). Federal State Statistics Service. http://perepis2002.ru/ct/html/TOM_01_03.htm. Retrieved 2008-10-17.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 Constitution, Article 6
- ↑ Bashkortostanstat. "Basic parameters of Bashkortostan Republic". http://www.bashstat.ru/bashdigital/region15/DocLib/%D0%A0%D0%91_%20%D0%B2%20%D1%86%D0%B5%D0%BB%D0%BE%D0%BC.htm. Retrieved 2008-05-17.
- ↑ (XLS) National Composition of Population for Regions of the Russian Federation. 2002 Russian All-Population Census. 2002. http://www.perepis2002.ru/ct/doc/English/4-2.xls. Retrieved 2006-07-20.
- ↑ Russian Census 2002. 6. Владение языками (кроме русского) населением отдельных национальностей по республикам, автономной области и автономным округам Российской Федерации(Knowledge of languages other than Russian by the population of republics, autonomous oblast and autonomous districts)(Russian)
- ↑ "Bashkortostan Jews Centered", Dateline World Jewry, World Jewish Congress, July/August 2008
Sources
- №ВС-22/15 24 декабря 1993 г. «Конституция Республики Башкортостан», в ред. Закона №23-з от 18 сентября 2008 г. (#VS-22/15 December 24, 1993 Constitution of the Republic of Bashkortostan, as amended by the Law #23-z of September 18, 2008. ).
Further reading
- Ilishev, Ildus G. (December 1998). "Russian federalism: Political, legal, and ethnolingual aspects — a view from the republic of Bashkortostan". Nationalities Papers 26 (4): 723–759. doi:10.1080/00905999808408597.
External links
- (Russian) Official website of Bashkortostan
- (English) Official website of Bashkortostan
- National anthem of the Republic of Bashkortostan (mp3)
- (English) "Bashinform" news agency
- (English) Links to English-language sites of Bashkortostan Republic and Ufa City
- (English) Official website on the 450th anniversary of Bashkortostan's voluntary joining Russia
- (English) Ministry for foreign economic relations and trade of the Republic of Bashkortostan
- (English) (Russian) Bashkortostan Export Portal
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
